open 10 am - 7 pm
laboratory is closed
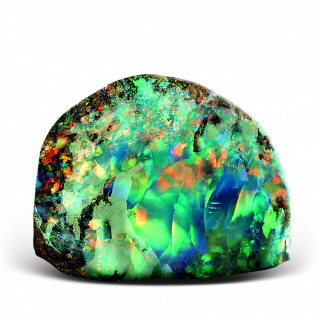
Opal
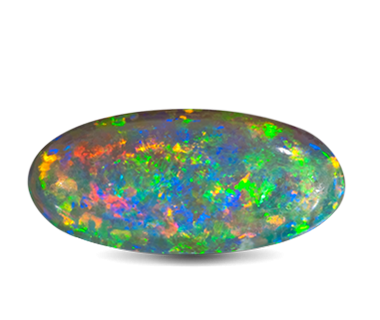
Opal is a mineraloid - hydrated amorphous form for silica. The Russian name is adapted from the Latin "opalus" is the name of this mineral, distorted from the Sanskrit "उपल (upalaḥ)" - "stone". Opals have a variety of colors from black and white to yellow, red, pink, green, blue and violet.
Chemistry: SiO2•nH2O;
Crystal system: none, amorphous;
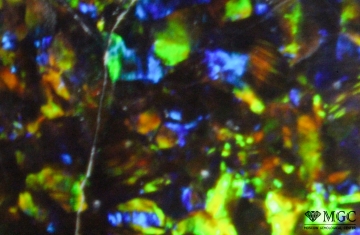
Color: "Common" opal, which is essentially a kind of rock, displays play-of-color from colorless and white to black and from red to purple. "Precious" opal shows a not so variable play colors: additional colors (opalescence). The main colors of "precious" opal are colorless, white, gray, black, brown, yellow, orange, and red. Additional colors are shown in opalescence - from blue to red. The main color is due to the saturation of opal chromophore impurities - mineral inclusions, salts of iron, manganese, chromium, nickel, copper and others. Additional colors ordered silica spheres produce the internal colors by causing the interference and diffraction of light passing through the microstructure of the opal. The regularity of the sizes and the packing of these spheres determines the quality of precious opal. The colors that are observed are determined by the spacing between the planes and the orientation of planes with respect to the incident light.
Identification properties
| Physical properties | |
|---|---|
| Mohs hardness: | 5.5 – 6.5 |
| Density: | 1.75 – 2.25 g/cm3 |
| Cleavage: | imperfect |
| Fracture: | Uneven, even, conchoidal |
| Optical properties | |
|---|---|
| Optical character: | isotropic |
| Refractive Index: | 1.370 – 1.470 |
| Birefringence: | none |
| Pleochroism: | none |
| Dispertion: | very weak |
| Luster: | vitreous |
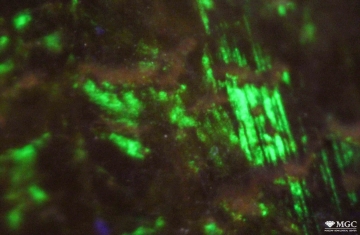
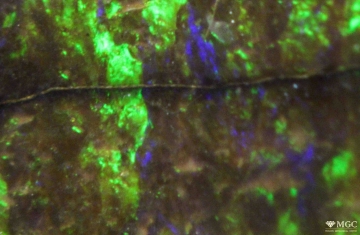
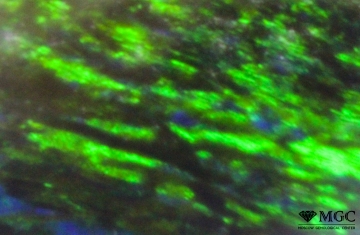
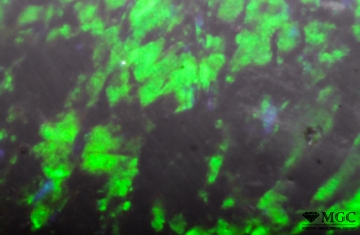
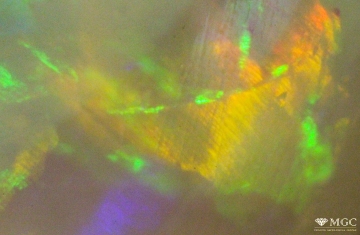
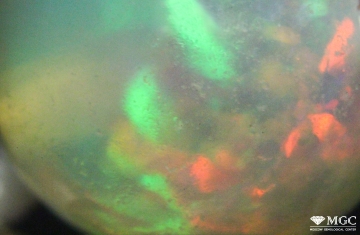
Inclusions and structural inhomogeneities



Gem basic treatments
| Treatment | Goal |
|---|---|
| Anthracolithization | Making the main background black |
| Impregnation with silica, glass or polymer compositions | Removing of porosity and opalescence enhancing |
| Impregnation with polymer compounds to fill the open cavities (glueing of fractures) | Improving the apparent clarity of gem material |
| Various color agents treatment | Altering and improving the apparent clarity and color of gem material |
Synthetic or Imitation gem materials
Opals of all varieties have been synthesized by methods of precipitation of colloidal solutions.
The most commonly encountered synthetic opal is as follows:
- opalescent glass;
- opalescent polymeric composition;
- doublets and triplets with natural and synthetic opal.
Inclusions and structural inhomogeneities