En
10:00 - 19:00
Monday - Thursday
open 10 am - 7 pm
open 10 am - 7 pm
✱
Friday - Sunday
laboratory is closed
laboratory is closed
Citrine

Citrine is a variety of quartz (α-quartz) colored in a wide range of yellow color. The name is derived from the Latin word "citrus" which means a lemon, a lemon-like citron, distinctive yellow color.
Chemistry: SiO2;
Crystal system: Trigonal, Trigonally-trapezohedral crystal class (point symmetry group);
Color: Yellow, greenish-yellow, orange-yellow to orange, with smoky hue.
Yellow color is due to ferric Fe3+ impurities in the crystal structure.
Identification properties
| Physical properties | |
|---|---|
| Mohs hardness: | 7 |
| Density: | 2.66±0.01 g/cm3 |
| Cleavage: | imperfect |
| Fracture: | conchoidal |
| Optical properties | |
|---|---|
| Optical character: | anisotropic, uniaxial, positive |
| Refractive Index: | no =1.544, ne =1.553 |
| Birefringence: | 0.009 |
| Pleochroism: | weak to intensive yellow tones |
| Dispertion: | 0.013(BG) |
| Luster: | vitreous |
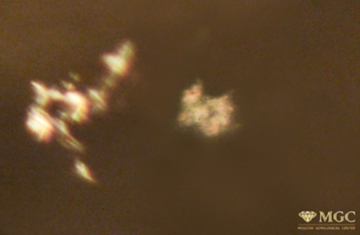
Inclusions and structural inhomogeneities

Mineral inclusions in natural citrine (deposit Volodarsk-Volynskoe, Ukraine). View mode - dark field lighting

Mineral inclusions in natural citrine (deposit Volodarsk-Volynskoe, Ukraine). View mode - dark field lighting
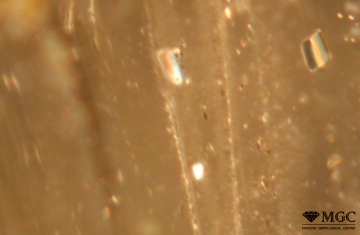
Tubular veil of mineral inclusions in natural citrine (deposit Volodarsk-Volynskoe, Ukraine). View mode - dark field lighting

Gas-liquid inclusions in natural citrine (deposit Volodarsk-Volynskoe, Ukraine). View mode - dark field lighting

Saw-like border of two-phase inclusion in natural citrine. View mode - dark field lighting
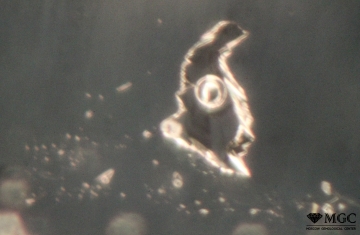
Three-phase inclusion in natural citrine. View mode - dark field lighting
Gem basic treatments
| Treatment | Goal |
|---|---|
| Heat treatment (in the temperature range above 300°С) | Removing the smoky and brownish hue |
Inclusions and structural inhomogeneities
Synthetic or Imitation gem materials
Synthetic citrine for the jewelry industry is produced by several methods of hydrothermal technique, based on the principle of temperature gradient.
The most commonly encountered synthetic citrine is as follows:
- colorless quartz, irradiation treated with the heat treatment followed;
- surface-colored quartz;
- quartz treated by "ion impregnation" - very rarely;
- doublet: quartz + glass;
- color glass
Inclusions and structural inhomogeneities
mgc-labs.ru © 2014–2024
All rights reserved