open 10 am - 7 pm
laboratory is closed
Amber

Amber is the name of a lithified organogenic formation - a fossil resin of the superfamily (“department”, according to O. Martirosyan) of amber-like resins. Takde traditionally refers to amber fossil resins that do not contain succinic acid, but structurally close to amber, possessing similar technological properties.
The Russian name "amber" comes from the Lithuanian name of the stone - "gintaras".
Varieties of amber used in the manufacture of jewelry and jewelry, refer to the jewelry and gemstones. The source of the formation of amber was the resinous discharge of conifers of the Araucaria, Pine and Cypress families.
Amber, like other fossil resins, is currently classified as a mineraloid from the point of view of mineral matter, but still there are publications in which amber belongs to minerals of organogenic origin.
A clear separation of amber and fossil resins, which are not amber, is possible only according to infrared spectrometry data.
At present, amber is attributed to: succinite, gedano-succinite, rumenite, burmit, shraufit, simetit, bekkerit, stantinit, as well as resins close to them — cheavinit, tsedarit, and others.
Color: yellow of various shades to brown (in oxidized and bituminous varieties). Often found whitish color due to the abundance of small gas bubbles in amber. Blue, green and other amber-colored stains are caused by microinclusions of a foreign mineral substance (for example, glauconite).
Identification properties
| Physical properties | |
|---|---|
| Mohs hardness: | 2-2,5 |
| Density: | 1,05 – 1,10 g/cm3 |
| Fracture: | conchoidal |
| Optical properties | |
|---|---|
| Optical character: | amorphous |
| Refractive Index: | 1,539-1,545 |
| Birefringence: | none, abnormal birefringence observed |
| Dichroism: | none |
| Luster: | glass, matte, resin |
| Transparency: | transparent to opaque |
Inclusions and structural inhomogeneities

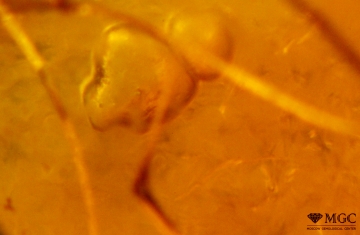


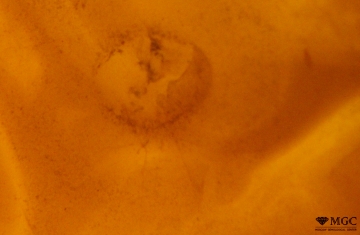
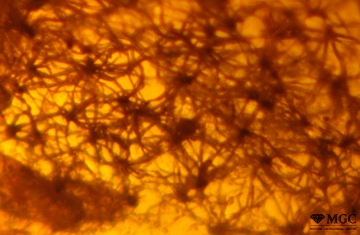
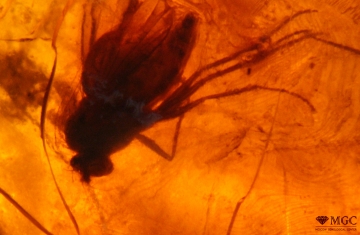
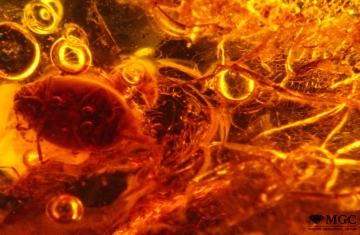

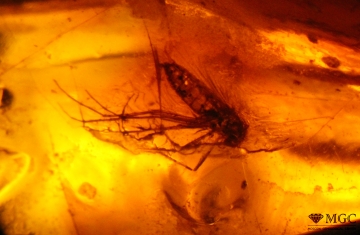
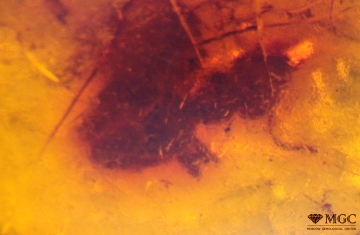



Gem basic treatments
| Treatment | Goal |
|---|---|
| Impregnation | Increased transparency |
| Impregnation of porous varieties | Color change |
| Surface staining | Color change |
| Diffusion treatment (thermochemical staining) | Color change |
| Heating | Color change |
| Heating | Increased transparency |
| Heating | Enhance decorative qualities |
| Agglomeration | Getting large blocks |
Inclusions and structural inhomogeneities
Agglomeration
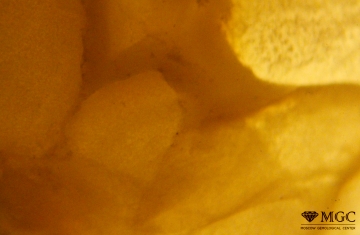

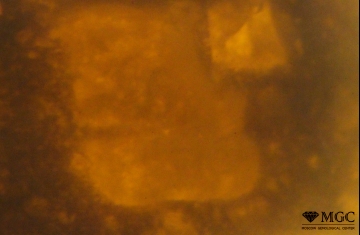
Synthetic or Imitation gem materials
Synthetic analogs of amber are not produced.
As imitations of amber are used:
- glass and ceramic compounds of artificial origin;
- polymeric compositions of artificial origin;
- modern resins;
- fossil resins ("immature" and retinite-like);
- composite compositions from polymer and small-sized amber fractions.


