open 10 am - 7 pm
laboratory is closed
Pearl

A pearl is a hard organogenic object produced within the soft tissue of mollusc shells. Although these may also be legitimately referred to as pearls by gemological labs - "elephant pearls", "bamboo pearls" and a number of others. The Russian name "pearl" comes from the Chinese name "zhen zhu" ("珍珠") through Turkic borrowing.
Pearl used in the jewelry manufacture has many varieties and differs in appearance, spread area and the biological variety of its producing mollusks.
Types of Pearls and their largest producers ➝
Chemical composition: Aragonite (CaCO3 – rhombic crystal structure) is composed of a combination of albuminous compounds (conchiolin - common chemical formula C32H48N2O11); internal parts of natural pearls sometimes are composed of a calcite composition.
Color: Nacreous pearls occur in a range of a white and "cream" color. Rarer gems having the basic pink, green, blue, lavender or gold colors, as well as the gray and black. The pearl primary color is defined by organic material in the mollusc habitat, and the characteristics of the irritants in the pearls composition (that generally depends on the biological characteristics of mollusc). Besides the basic color pearls there are additional colors (overtone), caused by the effect of light refraction at the boundary layers of nacre. Some colors are referred to as "orient" that is nacreous play of additional colors.
Typical commercial colors of non-nacreous pearls are white, pink (to red-purple), yellow, orange, purple and violet, as there are colors, commonly widespread, but colors that are relevant to the jewelry are gray, brown to black, and colors with dirty shades of gray and brown tones. The color of non-nacreous pearls due to the color of albuminous compounds that are part of the shell (and participating in the pearls cultivation), and irritants the mollusc habitat.
Identification properties
| Physical properties | |
|---|---|
| Mohs hardness: | 2.5-5 |
| Density: | 2.60 – 2.85 g/cm3 |
| Cleavage: | none |
| Fracture: | uneven |
| Optical properties | |
|---|---|
| Optical character: | microcrystalline matter* |
| Refractive Index: | 1.52 – 1.69 |
| Birefringence: | 0.156 |
| Pleochroism: | none |
| Dispertion: | none |
| Luster: | mother-of-pearl |
* Sometimes anomalously biaxial (which refers to twins, and distorted crystals).
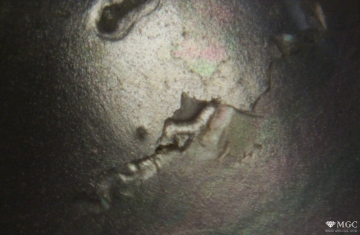
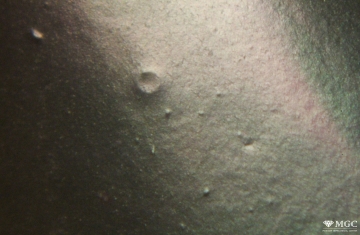
Inclusions and structural inhomogeneities
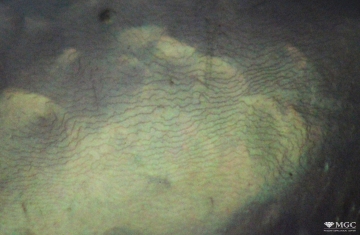
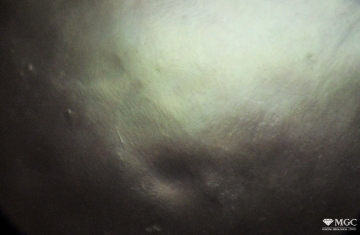
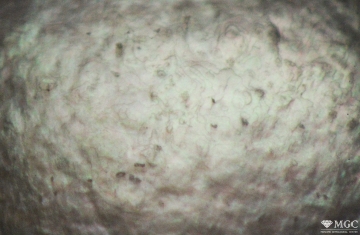

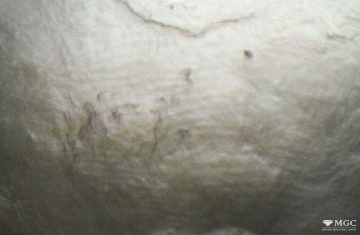
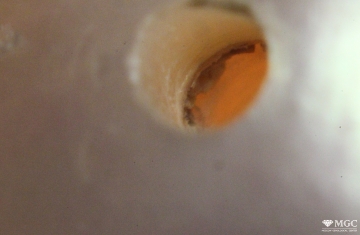
Gem basic treatments
| Treatment | Goal |
|---|---|
| Surface polishing | Polishing technique is applied to remove some surface blemishes and increase luster (unlike the polishing applied to all pearls in order to remove the surface microlayers found during formation, crushed peels and having undesirable spotting |
| Deep bleaching of the pearl surface | Altering the undesirable shade of the nacre (unlike the bleaching procedure applied to most white pearls in order to remove the spottiness of the surface layer caused by the mollusk organic residues) |
| Dissolution and/or exfoliation of the surface layer | Removing the undesirable hue of nacre |
| Drilling | Removing the surface defects |
| Impregnation of the pearl surface (oiling) | Preventing cracking of the surface layer |
| Impregnation of the pearl surface (waxing) | Filling of surface small defects and removing of porosity |
| Impregnation of pearls with different agents (filling) | Stabilization and/or covering the cracks |
| Dyeing the pearls (during its growth) in order to alter the color of pearls | Altering the pearl body |
| Irradiation treatment | Altering the pearl color |
| Heat treatment | Getting a brown (chocolate) color |
| Surface coating by applying a various coloring agent | Improving the visual perception of color, luster, and quality. |
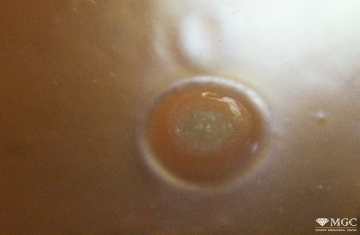
Inclusions and structural inhomogeneities
Dyeing

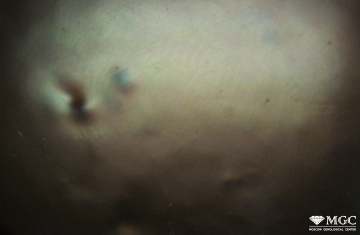
Synthetic or Imitation gem materials
Imitation pearls are man-made objects that are designed to resemble natural pearls since ancient times, constantly improving in technological and material terms.
Varieties of natural or cultured pearls imitation include:
- bathed pearls (for example: pearls - "Mabe" with internal filling);
- plastic core coated without pearlescent material;
- glass bead dipped or sprayed without pearlescent material;
- plastic core coated with pearlescent material;
- glass bead dipped or sprayed with pearlescent material;
- glass bead dipped or sprayed with pearlescent material (Majorica pearl);
- glass core coated with a mixture of plastic enamel;
- nacreous shell or any other shell core coated with a mixture of plastic enamel;
Inclusions and structural inhomogeneities