En
10:00 - 19:00
Monday - Thursday
open 10 am - 7 pm
open 10 am - 7 pm
✱
Friday - Sunday
laboratory is closed
laboratory is closed
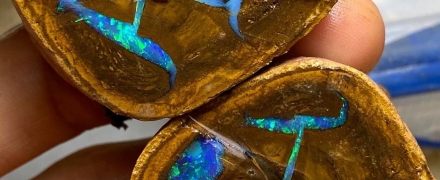
Radiation staining of topaz

The color of most natural topaz is associated with radiation defects in the structure of the crystal lattice of the stone. But, as a rule, natural stones do not possess residual radioactivity. Exceptions can be stones with internal inclusions of minerals with natural radioactivity, which is extremely rare in nature.
Topaz, containing in its composition only fluorine ion without admixture of hydroxyl-ion, are painted in blue and greenish-blue colors of varying degrees of intensity. For topaz containing hydroxyl-ion, characterized by yellow, brown and smoky-pink color. At the same time, often undesirable yellow and smoky shades are eliminated by annealing in the temperature range from 150 to 400 ° C, which is not affected by the intensity of the blue color in such stones.
Artificial radiation staining of minerals appeared in 1904, when the English physicist William Crookes (William Crookes, 1832-1919) stained diamonds by contact with radium salts. The first reliable report on radiation staining of topaz in the laboratory was made by Kurt Nassau (Kurt Nassau, born 1927-2010) in 1980 on the pages of the periodical Gems & Gemology, and then developed by Robert Crowningshild (George Robert Crowningshield, 1919-2006) in 1981 Later, in 1989, Charles E. Ashbaugh III, on the pages of the same periodical, described the process of radiation staining of several types of jewelry stones and noted the presence of residual radioactivity. In this regard, the laboratories of the Gemological Institute of America (GIA) from 1991 to 2006 provided services for the detection of residual or natural radioactivity of jewelry stones.
Radiation coloring of topaz, obtained in laboratory and industrial conditions, as well as in nature, is manifested in shades of yellow, smoky-pink (“wine”), as well as blue and green colors.
Radiation treatment of topaz is carried out by the following factors:
- Gamma radiation - exposure to electromagnetic waves of high frequency and energy from a source of Co-60 or Cs-137. Such processing does not leave residual radioactivity, and is used for industrial food processing, as well as sterilization of medical equipment;
- Beta-radiation - the effect of the flow of electron radiation. This treatment contributes to the formation of residual radioactivity, but recently little has been used because of the need for constant cooling of the mineral to be upgraded;
- The combined effect of the flux of neutron radiation and gamma rays. Such processing allows to achieve the most intense color, but contributes to the formation of residual radioactivity.
Typically, the period of reduction of residual radioactivity to an acceptable level ranges from several weeks to several months, but in some cases a high level may persist for quite a long time.
As a rule, all stones set in jewelry with radiation-modified color should undergo sanitary control, but occasional unwanted exceptions are possible. Therefore, where there is a suspicion of residual radioactivity, it is necessary to measure its level with a radiometer.
In addition to topaz, beryls (usually intense yellow varieties, aquamarines and Maksis beryls, some pink beryls), agates, cornelians, quartz (both natural and synthetic), tourmalines (red and yellow varieties), diamonds, and amblygonite are subjected to radiation staining. , apatite, chrysoberyl, spodumene (kunzite and hyddenite), pearls, corundum (ruby and sapphires).
It should also be borne in mind about the presence of natural radioactivity of minerals, which may have inclusions in zircons, some sapphires and garnets.
Remember! Your health is in your hands!
Topaz, containing in its composition only fluorine ion without admixture of hydroxyl-ion, are painted in blue and greenish-blue colors of varying degrees of intensity. For topaz containing hydroxyl-ion, characterized by yellow, brown and smoky-pink color. At the same time, often undesirable yellow and smoky shades are eliminated by annealing in the temperature range from 150 to 400 ° C, which is not affected by the intensity of the blue color in such stones.
Artificial radiation staining of minerals appeared in 1904, when the English physicist William Crookes (William Crookes, 1832-1919) stained diamonds by contact with radium salts. The first reliable report on radiation staining of topaz in the laboratory was made by Kurt Nassau (Kurt Nassau, born 1927-2010) in 1980 on the pages of the periodical Gems & Gemology, and then developed by Robert Crowningshild (George Robert Crowningshield, 1919-2006) in 1981 Later, in 1989, Charles E. Ashbaugh III, on the pages of the same periodical, described the process of radiation staining of several types of jewelry stones and noted the presence of residual radioactivity. In this regard, the laboratories of the Gemological Institute of America (GIA) from 1991 to 2006 provided services for the detection of residual or natural radioactivity of jewelry stones.
Radiation coloring of topaz, obtained in laboratory and industrial conditions, as well as in nature, is manifested in shades of yellow, smoky-pink (“wine”), as well as blue and green colors.
Radiation treatment of topaz is carried out by the following factors:
- Gamma radiation - exposure to electromagnetic waves of high frequency and energy from a source of Co-60 or Cs-137. Such processing does not leave residual radioactivity, and is used for industrial food processing, as well as sterilization of medical equipment;
- Beta-radiation - the effect of the flow of electron radiation. This treatment contributes to the formation of residual radioactivity, but recently little has been used because of the need for constant cooling of the mineral to be upgraded;
- The combined effect of the flux of neutron radiation and gamma rays. Such processing allows to achieve the most intense color, but contributes to the formation of residual radioactivity.
Typically, the period of reduction of residual radioactivity to an acceptable level ranges from several weeks to several months, but in some cases a high level may persist for quite a long time.
As a rule, all stones set in jewelry with radiation-modified color should undergo sanitary control, but occasional unwanted exceptions are possible. Therefore, where there is a suspicion of residual radioactivity, it is necessary to measure its level with a radiometer.
In addition to topaz, beryls (usually intense yellow varieties, aquamarines and Maksis beryls, some pink beryls), agates, cornelians, quartz (both natural and synthetic), tourmalines (red and yellow varieties), diamonds, and amblygonite are subjected to radiation staining. , apatite, chrysoberyl, spodumene (kunzite and hyddenite), pearls, corundum (ruby and sapphires).
It should also be borne in mind about the presence of natural radioactivity of minerals, which may have inclusions in zircons, some sapphires and garnets.
Remember! Your health is in your hands!
Other articles
mgc-labs.ru © 2014–2024
All rights reserved