open 10 am - 7 pm
laboratory is closed
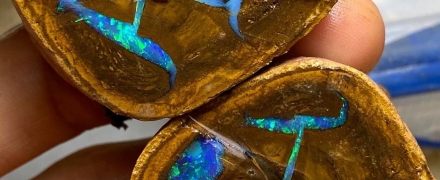
Types of inclusions in minerals

Inclusions in stones is one of the diagnostic signs, because a detailed study of them can often help establish the nature of origin, the presence of external influences (refinement), and sometimes even the deposit and conditions for stone formation.
The inclusions themselves can be completely different in size and shape, and in composition are divided into solid, liquid and gas-liquid.
- Solid inclusions are small fragments of other minerals that were captured during or after stone growth. Sometimes it is these inclusions that can determine the color of the mineral;
- Liquid inclusions are cavities that are completely filled with a solution of one or another composition;
- Gas-liquid inclusions consist of a bubble of air and liquid and often occupy cavities that are negative crystals.
One-phase, two-phase, three-phase inclusions in minerals are also distinguished. In single-phase - the entire inclusion cavity is filled with liquid, in two-phase - there is a gas bubble in the cavity along with the liquid, and three-phase inclusions, in addition to liquid and gas, also contain a crystalline mineral. The composition of phases in inclusions can be quite diverse: the liquid phase can be represented by water, aqueous solutions or carbon dioxide, the solid phase is most often salt crystals - the most common are halite and sylvin, the composition of the gas phase of inclusions is still poorly studied, but there are assumptions that the bubble may contain carbon dioxide, hydrogen sulfide and water vapor.
According to the time of formation, inclusions in minerals are divided into protogenetic (relict), syngenetic and epigenetic. What does it mean?
- Protogenetic (relict) inclusions were formed before the mineral began to grow and were mechanical “obstacles” during its formation. An example of such inclusions is quartz “hairy” with numerous inclusions of rutile and black tourmaline.
- Syngenetic inclusions are inclusions that are formed together with the growth of the main crystal. An example of such inclusions are inclusions of olivine, pomegranate, and chromepenellides in diamond.
- Epigenetic inclusions are formed after the growth of the mineral and, in fact, have no genetic connection with it. So, for example, any fluid trapped in a mineral fracture can be considered an epigenetic inclusion.